Understanding the Prostate Gland: A Core Component of Male Reproductive Health
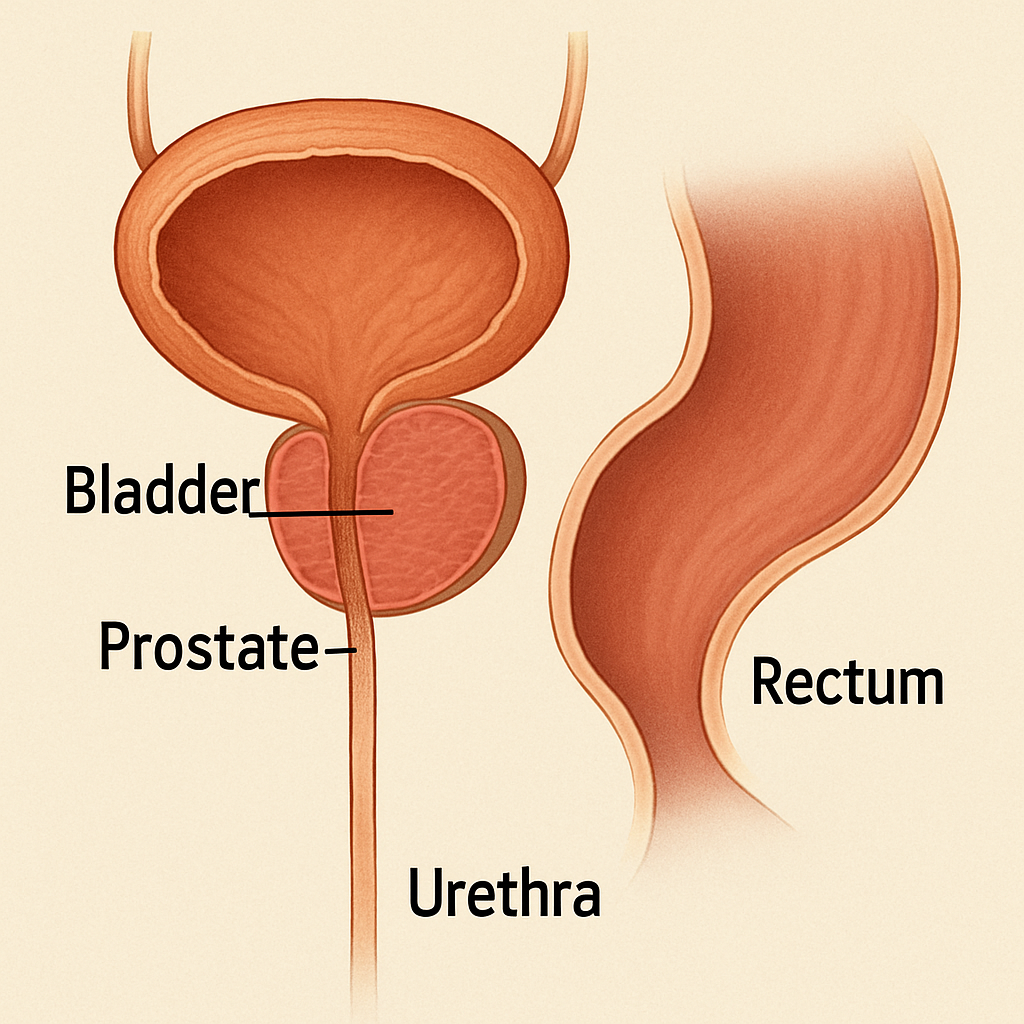
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum in men. It surrounds part of the urethra, the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body. Despite its small size, the prostate plays an essential role in male fertility, urinary function, and overall reproductive health.
The Prostate’s Role in the Male Reproductive System
The prostate’s primary function is the production of seminal fluid, a nutrient-rich liquid that combines with sperm from the testicles to form semen. This fluid nourishes and protects sperm, increasing its motility and lifespan. Without the prostate, sperm would lack the optimal environment required for successful fertilization.
Prostate secretions include enzymes, zinc, and citric acid, which create an alkaline medium to neutralize the acidity of the vaginal tract, ensuring sperm viability. One key enzyme produced is prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which helps liquefy semen after ejaculation, allowing sperm to swim freely.
Hormonal Regulation and the Prostate
The growth and function of the prostate are closely linked to male sex hormones, particularly testosterone. Testosterone, produced by the testicles, is converted into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) within the prostate. This potent hormone stimulates the gland’s growth and contributes to the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
However, hormonal imbalances—especially elevated DHT levels—can lead to prostatic hypertrophy, or an enlarged prostate, which commonly affects men over the age of 50.
Why the Prostate Is Crucial to Urinary Health
Because the prostate encircles the urethra, its size directly influences urinary flow. When the prostate enlarges—a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)—it can constrict the urethra and interfere with urination. Common symptoms include:
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine stream
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- A feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
BPH is non-cancerous, but it significantly affects quality of life. In severe cases, it can lead to urinary retention, bladder infections, or kidney damage.
Prostate Health and Cancer Risk
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men, particularly those over the age of 65. It begins when abnormal cells in the prostate grow uncontrollably, often without noticeable symptoms in its early stages.
Early detection through PSA testing and digital rectal examination (DRE) is critical. While PSA levels can be elevated for reasons other than cancer, persistently high levels warrant further investigation. Prostate biopsies and imaging tests can confirm the presence of malignancy.
When detected early, prostate cancer is highly treatable through surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy. Regular screening is essential, especially for men with a family history of the disease or those of African-American descent, who are statistically at higher risk.
Maintaining a Healthy Prostate
Several lifestyle choices support prostate health and may reduce the risk of enlargement or cancer:
- Diet rich in antioxidants: Tomatoes (lycopene), green tea, berries, cruciferous vegetables
- Regular exercise: Improves hormone regulation and immune function
- Healthy weight management: Reduces inflammation and hormonal imbalances
- Limiting red meat and high-fat dairy: Associated with lower prostate cancer risk
- Routine screenings: Especially after age 50, or earlier if risk factors exist
The Psychological and Sexual Impact of Prostate Issues
Prostate disorders don’t just impact physical health—they can affect sexual function and mental well-being. Conditions such as BPH and prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate) may lead to erectile dysfunction, pain during ejaculation, or reduced libido. These symptoms often trigger anxiety, depression, and a decline in self-esteem.
Timely intervention and open communication with healthcare providers are key. Treatments range from medications and lifestyle adjustments to surgical options, all aimed at preserving quality of life and sexual wellness.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Prostate Health Across the Lifespan
The prostate gland may be small, but its impact on a man’s life is immense. From supporting fertility and ensuring urinary flow to its susceptibility to enlargement and cancer, this gland deserves continuous attention. Through proactive health choices, regular screenings, and informed medical care, men can take control of their prostate health and maintain well-being throughout every stage of life.
Read Our other articles: